10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Small Diaphragm Pump?
When selecting a small diaphragm pump, users often face challenges. Understanding the key elements can significantly impact performance and longevity. According to the 2022 Small Pump Market Report, around 45% of users experience technical failures due to incorrect pump selection.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Hart, a leading researcher in fluid dynamics, emphasized, "Choosing the right small diaphragm pump is critical for optimal efficiency." A small diaphragm pump must meet specific operational requirements, including flow rate and chemical compatibility.
Details like size, materials, and power source also matter. For instance, a pump made of corrosive-resistant material ensures longer service life. Yet, noted common errors include underestimating maintenance needs and overlooking manufacturer specifications. Reflecting on these aspects can lead to better decision-making and ultimately enhance system reliability.
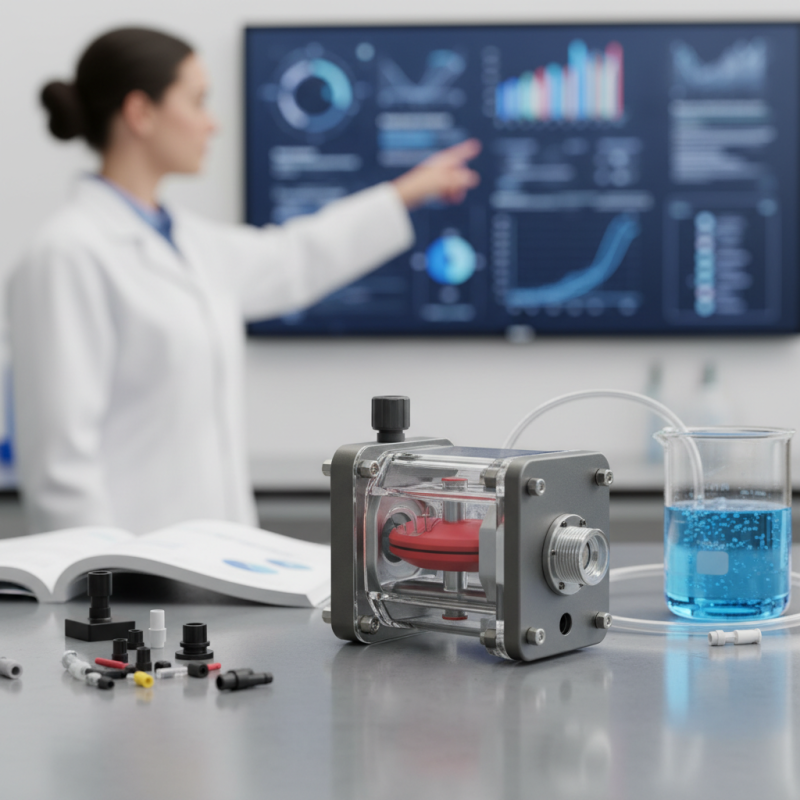

Key Considerations for Small Diaphragm Pump Selection

When selecting a small diaphragm pump, understanding key considerations is vital. First, think about the application. Pumps used in food processing and chemical transfer have different requirements. A study by the Hydraulic Institute shows that efficiency and flow rates directly impact operational costs. Knowing the specific needs will help narrow down the options.
Another aspect is material choice. Diaphragms can be made from rubber, PTFE, or other composites. Each material has its durability and chemical compatibility characteristics. Inappropriate material selection could lead to pump failure. A survey revealed that 30% of pump failures stemmed from improper material choices. Users must ensure materials align with the fluids being pumped.
Lastly, check the size and weight of the pump. Compact designs are often beneficial in space-restricted environments but may sacrifice performance. Be mindful of the trade-offs. Many users report that a smaller pump struggles with high-viscosity fluids, highlighting the importance of balancing size with capability.
Understanding the Application Requirements for Your Pump
Choosing the right small diaphragm pump begins with understanding your application requirements. What will the pump be used for? Is it for transferring liquids, or perhaps for gas? These questions shape your pump selection. Assess the nature of the fluids involved. Are they corrosive, viscous, or abrasive? Documenting these characteristics can prevent costly mistakes.
Flow rate is crucial too. Do you need a steady flow or intermittent bursts? Consider the pressure requirements as well. Does the system operate under high pressure or low vacuum? Each scenario demands different specifications. Pay attention to the pump material, especially when dealing with unique fluids. This detail might seem minor, but it can vastly affect pump longevity.
Lastly, environmental factors may influence your choice. Temperature variations can alter performance. Inconsistent ambient conditions might require robust solutions. Reflect on the entire operation’s needs before making a decision. This thought process isn’t always straightforward, and multiple prototypes could be necessary. Take time to evaluate options and test them practically.
Evaluating Pump Materials and Compatibility with Fluids

Choosing the right materials for a small diaphragm pump is crucial. The pump's material must match the fluids it will handle. For instance, if you are pumping corrosive substances, materials like certain plastics or stainless steel may be necessary. If you overlook this, you could face pump degradation or failure. The cost of replacing a ruined pump can be significant.
Compatibility extends beyond just materials. Consider the temperature and pressure of the fluids. Some materials may perform poorly under extreme conditions. You may think that all plastics are similar, but their performance can vary greatly. It's essential to ask questions and do thorough research before making a choice. Ignoring specifics can lead to costly mistakes.
Another consideration is the fluid's viscosity. Thicker fluids require different pumps than thinner ones. A pump unsuitable for the task may lead to inefficiencies. It’s easy to assume one pump fits all, but that's rarely the case. Reflect on the details before deciding. Understand your needs fully to avoid issues later.
Assessing Flow Rate and Pressure Needs for Optimal Performance
When choosing a small diaphragm pump, assessing specific flow rate and pressure needs is crucial. The right pump can enhance your project's efficiency. Think about the tasks it needs to accomplish. Will it transport liquids swiftly? Or is precision more important? Understanding your requirements is the key step.
Tip: Calculate your flow rate. Identify how much liquid you need to move within a given time. This helps in choosing a pump that matches your needs. Also, remember that pressure matters too. Verify the maximum pressure your application requires. Too little pressure can lead to ineffective performance.
In addition, evaluate the pump's materials. Different liquids may require specific materials to prevent corrosion. A mismatch could lead to leaks or failures. Think about the environment as well. Is it clean, or is there dust and debris? Improper conditions can reduce pump lifespan. Consider these factors carefully for a successful choice.
10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Small Diaphragm Pump
| Tip No. | Tip Description | Recommended Action | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Determine Flow Rate Requirements | Calculate the required flow rate based on application needs. | Consider peak flow demands. |
| 2 | Assess Pressure Needs | Identify the necessary discharge pressure for your application. | Account for system losses. |
| 3 | Evaluate Fluid Compatibility | Ensure materials are suitable for the fluids being pumped. | Protect against corrosion and chemical reactions. |
| 4 | Check for Pulsation Requirements | Determine if pulsation dampening is necessary. | Influences the system's performance and fluid delivery. |
| 5 | Consider Operating Temperature | Select pumps that can withstand the application's temperature ranges. | Avoid material degradation. |
| 6 | Examine Size and Weight Constraints | Ensure the pump fits within designated space requirements. | Consider portability needs. |
| 7 | Analyze Power Supply Options | Evaluate electricity or pneumatic power requirements. | Consider available power sources. |
| 8 | Review Maintenance Needs | Check the pump's ease of maintenance and service. | Plan for routine maintenance schedules. |
| 9 | Calculate Total Cost of Ownership | Evaluate purchase price, installation, and operational costs. | Consider long-term expenses. |
| 10 | Seek Expert Advice | Consult with industry experts to validate choices. | Gain insights into best practices and product performance. |
Comparing Pump Sizes and Configurations for Space Efficiency
When selecting a small diaphragm pump, size and configuration are critical. Space efficiency can make or break your setup.
Smaller pumps often come with incredibly compact designs. They can fit into tight spots, making them perfect for limited spaces. A pump that is too large can lead to
wasted space and decreased efficiency.
Consider the configuration as well. Some pumps are designed with specific orientations in mind.
Vertical configurations might suit a tall, narrow space. In contrast,
horizontal configurations work well for wider setups. Determining how the pump fits in relation to other equipment
is crucial. Forgetting this can lead to awkward arrangements that hinder performance.
There are trade-offs to consider. A smaller pump may not deliver the same flow rate as a larger one.
This can limit its effectiveness for certain applications. Reflect on what you prioritize—space or performance?
It’s a delicate balance. Even with the right dimensions, the wrong configuration can produce inefficiencies.
Investing time to analyze these factors ensures you avoid common pitfalls in pump selection.
Related Posts
-

Maximizing Efficiency with Small Diaphragm Pumps in Pharmaceutical Applications
-
Unlocking Efficiency: The Science Behind Performance Optimization in Electric Double Diaphragm Pumps
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right 3 Diaphragm Pump for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Advantages of Pneumatic Diaphragm Pumps in Industrial Applications
-
Why the Wilden Diaphragm Pump is the Best Choice for Reliable Fluid Transfer in Industrial Applications
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Air Operated Double Diaphragm Pump
 |
Need Help? Call Us 203-740-1877 
|
We're ready to help identify, size and spec your pumps, filters |
All Products
Reliable Equipment Sales, LLC
Pumps, Parts, and Equipment – Guidance Included
103 Hempel Drive
Wolcott, CT 06716
Telephone: 203-740-1877
Toll Free Fax: 866-523-1693
Email: sale@rewritertool.com


