What is a Magnetic Pump and How Does It Work?
Magnetic pumps have gained significant traction in various industries due to their unique design and functionality. According to a recent market analysis by Grand View Research, the global magnetic pump market is expected to reach $1.62 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increasing demand for efficient, reliable, and leak-free pumping solutions. As John Smith, a leading expert in fluid dynamics, noted, "Magnetic pumps are revolutionizing how we handle liquids, especially in sensitive environments."
These pumps utilize magnetic fields to transfer energy, creating a contactless operation that minimizes wear and tear. Their non-invasive nature lowers the risk of contamination, making them ideal for chemical processing and pharmaceutical applications. Despite their advantages, magnetic pumps are not without challenges. They can be more expensive upfront, and not all applications may warrant their use.
In real-world applications, the efficiency of a magnetic pump can vary. Factors such as viscosity, flow rate, and system design play crucial roles. While these pumps promise higher performance, they require careful consideration and expertise to implement effectively. In the end, understanding the nuances of how a magnetic pump operates is essential for maximizing its benefits in various industrial settings.

What is a Magnetic Pump?
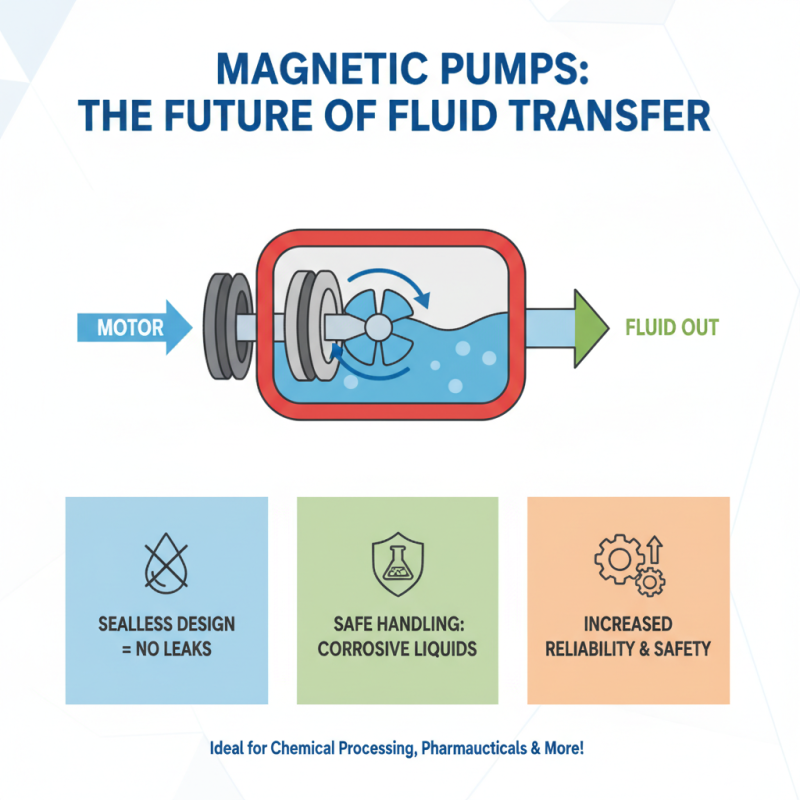
A magnetic pump is a type of pump that utilizes magnetic forces to move fluids. It consists of two main components: a magnetic drive and the pump casing. The magnetic drive creates a rotating magnetic field, which turns the impeller inside the casing. This design eliminates the need for a traditional shaft and mechanical seals. The result is a system that reduces leaks and maintenance needs.
According to a recent industry report from the Fluid Handling sector, magnetic pumps can achieve efficiency ratings of over 80%. This efficiency is beneficial in applications where energy consumption costs are high. Moreover, magnetic pumps are ideal for handling corrosive or hazardous fluids. They minimize contact with the environment, which is crucial for safety and sustainability. However, there are some limitations. These pumps struggle with high-viscosity fluids and can be more expensive to install.
The market for magnetic pumps continues to grow. In fact, it was estimated to reach $2 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increased demand for reliable and environmentally friendly pumping solutions. Still, potential users should consider their specific applications carefully. It's important to assess fluid characteristics, required flow rates, and operating conditions before making a decision. Awareness of these factors can lead to better efficiency and performance in the long run.
Principle of Operation for Magnetic Pumps
Magnetic pumps operate based on a simple but effective principle. They use magnetic fields to transfer rotational energy. This avoids traditional seals, reducing leaks and maintenance. The basic components include a magnetic rotor and an impeller. The rotor generates a magnetic field that drives the impeller. This results in smooth fluid flow without direct contact between components.
Data from industry reports suggest that magnetic pumps can achieve efficiencies over 80%. This is significant compared to conventional pumps. Their design minimizes wear and tear, extending lifespan. However, they are not without drawbacks. Their initial costs can be higher and they may not handle high-viscosity fluids well.
Tips: When selecting a magnetic pump, consider your fluid's properties. Avoid using these pumps for fluids containing solids. Routine inspections can prevent unexpected failures. Always account for the pump's magnetic capabilities. The market offers a variety of models, but understanding your specific needs is crucial.
Performance Characteristics of Magnetic Pumps
Components of a Magnetic Pump
A magnetic pump is an innovative device that uses magnets to move fluids. Understanding its components is essential for better operation and maintenance. The main elements include the motor, magnetic drive, and pump casing.
The motor generates magnetic forces. This force is transmitted to the impeller via a magnetic coupling. The impeller, located in the pump casing, moves the fluid. This design prevents leaks, which is a common issue in traditional pumps. The pump casing protects the internal components and provides structural support.
**Tip:** Regularly check the magnetic coupling for wear. If it shows signs of damage, consider replacing it sooner rather than later.
Another crucial part is the bearings. Quality bearings ensure smooth operation. They reduce friction and wear over time. However, not all bearings are created equal. Using subpar materials can lead to premature failure.
**Tip:** Invest in quality bearings to enhance longevity. This small change can save you from significant repairs down the line. A proactive approach will help maintain your pump's efficiency.
What is a Magnetic Pump and How Does It Work? - Components of a Magnetic Pump
| Component | Function | Material | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Drive | Transmits torque from the motor to the impeller | Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, water treatment |
| Impeller | Moves the fluid by converting rotational energy | Plastic, Ceramic | Food processing, pharmaceuticals |
| Casing | Houses the internal components and provides safety | Polypropylene, PVC | Wastewater treatment, aquariums |
| Magnets | Creates the magnetic field necessary for operation | Neodymium | Industrial applications, cooling systems |
Advantages of Using Magnetic Pumps
Magnetic pumps are unique. They have no seals. This design prevents leaks, making them safer. They are widely used in various industries, such as chemical processing and food production. These pumps use magnetic fields to drive fluid movement. This makes them efficient and reliable.
One major advantage of magnetic pumps is energy efficiency. They often consume less energy than traditional pumps. This results in lower operational costs. Additionally, they are easy to maintain. With fewer moving parts, there’s less wear and tear.
**Tips:** Regular maintenance can further enhance their lifespan. Monitor the magnetic coupling for any signs of wear. This can prevent costly repairs later. Another tip is to ensure the pump is suitable for the fluid being handled. Some liquids can be corrosive or abrasive.
The installation process, while straightforward, requires attention. If not set up correctly, performance may suffer. Knowing the specific application and requirements can help in choosing the right pump. Remember, the right pump can save money and improve efficiency in the long run. Always think critically about your needs before making a choice.
Applications of Magnetic Pumps in Industry
Magnetic pumps are increasingly popular in various industries due to their unique abilities. They work using magnetic fields to transfer energy to fluids. Unlike traditional pumps, they have no seals. This reduces the risk of leaks significantly. In chemical processing, magnetic pumps handle corrosive substances safely. They protect both workers and the environment.
In the food industry, magnetic pumps ensure hygiene. They transport liquids without contaminating them. This is crucial for maintaining product quality. However, these pumps can struggle with high-viscosity fluids. Adjustments may be necessary to find the right flow rate.
Another application is in water treatment. Magnetic pumps manage sludge and other challenging materials. They help in maintaining clean water systems. Yet, their installation can be tricky. Proper training is essential for effective use. Overall, the adaptability of magnetic pumps shows promise, but there are limitations that must be acknowledged.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Best 55 Gallon Drum Transfer Pumps for Efficient Fluid Transfer
-

Understanding the Benefits of Using Electric Drum Pumps in Industrial Applications
-
What is a Diaphragm Pump and How Does it Work in Applications
-

How to Choose the Right Barrel Pump for Your Needs: A Complete Guide
-

Top 10 Best 30 Gallon Drum Pumps for Easy Liquid Transfer in 2023
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using a Barrel Hand Pump for Efficient Liquid Transfer
 |
Need Help? Call Us 203-740-1877 
|
We're ready to help identify, size and spec your pumps, filters |
All Products
Reliable Equipment Sales, LLC
Pumps, Parts, and Equipment – Guidance Included
103 Hempel Drive
Wolcott, CT 06716
Telephone: 203-740-1877
Toll Free Fax: 866-523-1693
Email: sale@rewritertool.com


